Less-skilled workers are liable to be among the first fired in a downturn. The June unemployment rate dropped a mere one percent but the labor force jumped up by 2673.

Unemployment Rate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
A study suggests recruiters struggle to sift through the many applications from job-seekersJun 2nd 2021WHEN THE supply of houses for.
Why unemployment rate remain high now. Thats the highest unemployment rate for the series going back to 1948 and also the biggest jump with the unemployment rate tripling in a month since March. A study suggests recruiters struggle to sift through the many applications from job-seekers Graphic detail. Lots of Americans want work.
Investors are cautiously trading ahead of the result while some economists are projecting a higher unemployment rate this time. T he evidence of a labor shortage comes both from hard numbers and from soft anecdotes. Another reason why unemployment can remain high even in a recovery.
But that is still nearly twice its pre-pandemic level. Again US will announce one of their main economy indicators unemployment rate this Friday 6 th August. This trend continued until the unemployment rate bottomed.
Ployment rates for Blacks and Hispanics remained in double digits at 158 percent and 129 percent respec-tively. Investors are cautiously trading ahead of the result while some economists are projecting a higher unemployment rate this time. Why is unemployment still so high despite some positive economic news.
The unemployment rate is expected to reach 72 per cent essentially remaining unchanged. Unemployment is a problem because it can create losses of income increases in expenditures and societal problems that negatively affect individuals and society as a whole. More than one in three workers is living in conditions of extreme poverty while almost three out of four workers are in vulnerable employment.
While June 2021s unemployment rate is significantly lower its still far from pre-pandemic levels. The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 148 in April 2020 the highest rate since 1948 as governments imposed restrictions to stop the spread of the coronavirus and businesses closed. Unemployment is at a 50-year low.
Why unemployment rate remain HIGH now. Costs generated by unemployment are considered dead losses as they do not create any gains or benefits. Barry Bosworth discusses the reasons so many Americans remain jobless saying that The problem is not.
This provided a hint into why the unemployment rate stayed stuck where it was in April. In April 2020 after governments shut down the economy the unemployment rate reached 148 the highest since the Great Depression. The unemployment rate for Asians was 73 percent not seasonally adjusted at the end of the year.
The labor force wasnt growing enough to fill the 2800 jobs created that month April. The purpose of that boost is to help laid-off workers replace. While layoffs increased during this recession they are not the primary cause of the nearly 10 percent unemployment rate.
In terms of the hard numbers. Workers with less education continued to experience a. One reason that SNAP enrollment may remain high for several years after a recession ends and the unemployment rate begins to decline is that people who find jobs with low wages and limited hours often will still be eligible for SNAP.
Even this very large official increase understates the increase in the unemployment rate from a historically-comparable perspective because it counts an extra 49 million people who were not at work for other reasons as employed and also because 63 million people have left the labor force since February more than would be expected even conditional on this large increase in unemployment. Right now Americans on unemployment benefits are entitled to an additional 600 federal weekly boost on top of their normal benefit. A second reason may be that the least-skilled workers are slower to be hired back.
Again US will announce one of their main economy indicators unemployment rate this Friday 6 th August. The main factor driving the unemployment rate so high. Since the onset of the covid-19 pandemic Americas unemployment rate has fallen sharply from 148 to 61.
Substantially higher unemployment rate than did better edu-. Based on surveys taken in late March 63 million people were not working because of a need to care for a child not in a school or day care center and a further 21 million were caring for an. The number of unemployed should increase by 1 million due to the regions high levels of labour force growth.
The low rate is not from an unusually high job-finding rate out of unemployment but rather an unusually low rate at which people enter unemployment. At the individual level unemployment has both immediate and long. Why unemployment rate remain HIGH now.
The low entry rate reflects a long-run downward trend likely due to population aging better job matches and other structural factors. Would we see the same problem in June 2017 we wondered.

Yes Unemployment Fell But The Recovery Seems To Be Slowing Down Fivethirtyeight

Philippines Unemployment Rate 2020 Statista
/UnemploymentandGDP2008-80ffa8c6bee640208888f8cc26cb38e2.jpg)
Unemployment And Recession What S The Relation

The California Economy Unemployment Update Public Policy Institute Of California
April Jobs Report Unemployment Hits 14 7 Us Economy Loses 20 5 Million Jobs

Yes Unemployment Fell But The Recovery Seems To Be Slowing Down Fivethirtyeight

Greece Unemployment Rate Greece Economy Forecast Outlook
Causes Of Unemployment In The United States Wikipedia

The Unemployment Impacts Of Covid 19 Lessons From The Great Recession

Yes Unemployment Fell But The Recovery Seems To Be Slowing Down Fivethirtyeight
/dotdash_Final_Okuns_Law_Economic_Growth_and_Unemployment_Oct_2020-01-2e5dd7aa7c194e14a82707b84b00d1a3.jpg)
Okun S Law Economic Growth And Unemployment
The Post Recession Labor Market An Incomplete Recovery Institute For Research On Labor And Employment
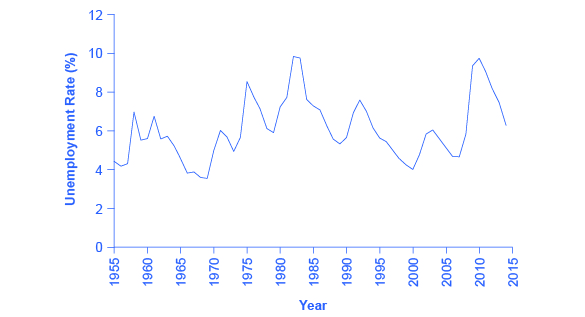
21 2 Patterns Of Unemployment Principles Of Economics
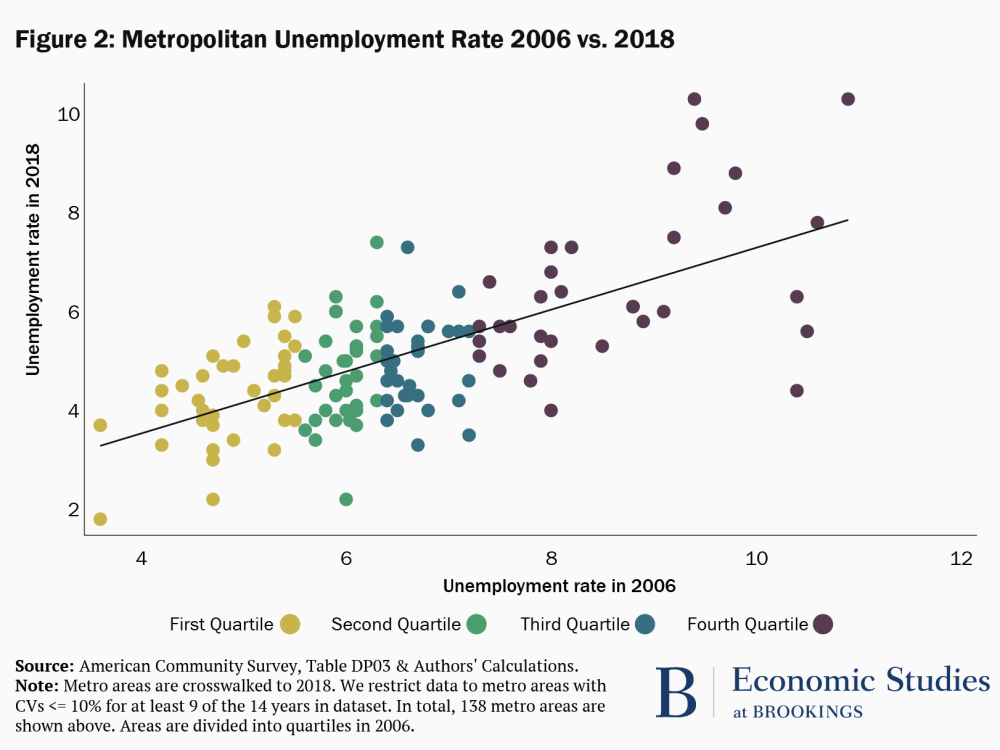
The Unemployment Impacts Of Covid 19 Lessons From The Great Recession

The California Economy Unemployment Update Public Policy Institute Of California
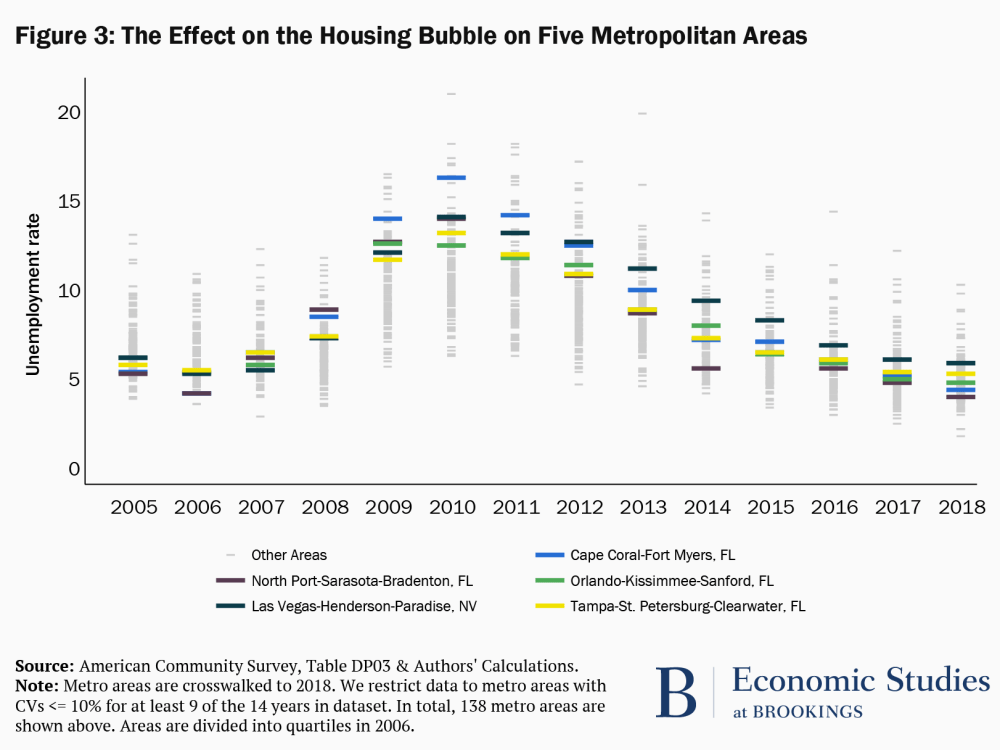
The Unemployment Impacts Of Covid 19 Lessons From The Great Recession
